Uterine Fibroids Symptoms: Identifying Uterine Tumor Signs And Treatment Options
If you are a woman, you may experience uterine fibroids at some point in your life. Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that can affect your quality of life if left untreated. It is important to understand what uterine fibroids are, why they matter, and how you can prevent and manage them.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in or on the uterus. These tumors vary in size and can affect the entire uterus or just a portion of it. According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, up to 80 percent of women will have uterine fibroids by age 50.

What Are the Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids?
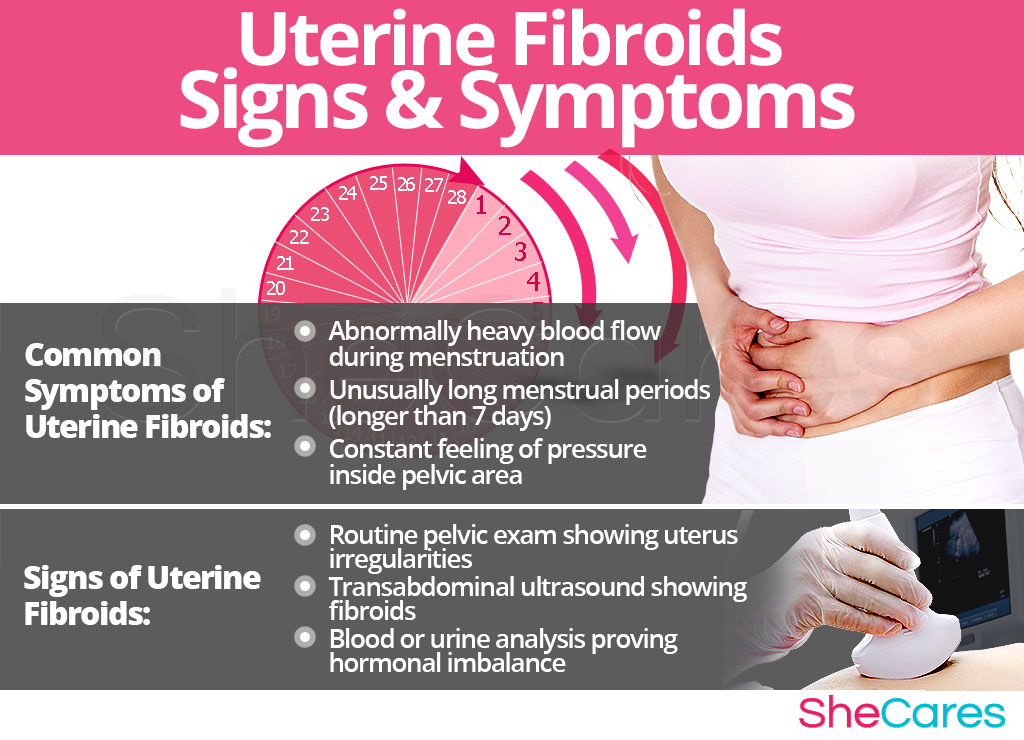
Uterine fibroids can cause a range of symptoms, or they may not cause any symptoms at all. Some common symptoms of uterine fibroids include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Painful periods
- Abdominal pressure
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Lower back pain
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty emptying bladder
Importance of Diagnosing and Treating Uterine Fibroids
If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, you should talk to your healthcare provider about uterine fibroids. Timely diagnosis and treatment is important for mitigating the impact of these benign tumors on your health and quality of life.
Uterine fibroids can interfere with your ability to get pregnant, cause significant pain and discomfort, and even lead to anemia due to excessive bleeding. Treatment options include medication, surgery, and minimally invasive procedures like uterine fibroid embolization.
Statistics on Uterine Fibroids
According to the National Institutes of Health, African American women are two to three times more likely to experience uterine fibroids than women of other racial and ethnic groups. Additionally, uterine fibroids tend to develop at an earlier age in African American women and are more likely to cause severe symptoms.
While age and genetics are the primary risk factors for developing uterine fibroids, other factors like obesity, hypertension, and stress can also contribute to their formation and growth.
Types of Uterine Fibroids
There are several types of uterine fibroids, each with different characteristics and treatment options. The most common types of uterine fibroids include:
- Intramural fibroids: These develop within the muscular wall of the uterus and may cause enlargement of the uterus and heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Subserosal fibroids: These grow on the outer wall of the uterus and may cause pelvic pain and pressure.
- Submucosal fibroids: These develop just beneath the lining of the uterus and can cause heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
- Pedunculated fibroids: These grow on a stalk-like structure outside the uterus or within the uterine cavity. They can become twisted and result in pain and other complications.

Risk Factors for Uterine Fibroids
While the exact cause of uterine fibroids is unknown, there are several factors that may increase a woman's risk of developing them. These risk factors include:
- Age: Uterine fibroids are more common in women over 30 years of age.
- Family history: If a woman's mother or sister has had uterine fibroids, her risk of developing them is higher.
- Race: African American women are more likely to develop fibroids than women of other ethnic backgrounds.
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase a woman's risk of developing fibroids.
Recognizing Early Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
It is important to recognize the early symptoms of uterine fibroids so that you can seek medical attention and receive an accurate diagnosis. Some of the early symptoms of uterine fibroids to watch for include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding or bleeding between periods
- Prolonged periods lasting more than a week
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Pelvic pressure or bloating
Diagnostic Tests for Uterine Fibroids
If your healthcare provider suspects that you have uterine fibroids, they may order diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis. Some common diagnostic tests for uterine fibroids include:
- Ultrasound: This uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the uterus and can detect fibroids.
- MRI: This uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the uterus and can detect fibroids.
- Hysteroscopy: This involves inserting a thin, lighted scope through the cervix to examine the uterus and can detect submucosal fibroids.
- Biopsy: This involves removing a small sample of tissue from the uterus for testing and can confirm the presence of fibroids.
Awareness and Prevention of Uterine Fibroids
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent uterine fibroids, there are several things women can do to reduce their risk of developing them. These include:
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet
- Staying physically active
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Managing stress levels
- Getting regular gynecological check-ups
Early Detection and Timely Treatment
Early detection and timely treatment of uterine fibroids is crucial for maintaining your overall health and well-being. If you experience any symptoms of uterine fibroids, talk to your healthcare provider about your options for diagnosis and treatment.
There are several treatment options available for uterine fibroids, including medication, surgery, and minimally invasive procedures like uterine fibroid embolization. Working with your healthcare provider to find the right treatment plan for you can help alleviate your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Support and Resources for Uterine Fibroids
If you have been diagnosed with uterine fibroids, there are several resources and support groups available to you. These organizations can provide information, resources, and emotional support to help you navigate your diagnosis and treatment.
Through education, awareness, and early detection, women can take important steps to protect their health and prevent the negative impacts of uterine fibroids. If you suspect you may have uterine fibroids, don’t wait to seek medical attention. Your health and well-being are too important to delay.
Komentar
Posting Komentar