Cervical Dysplasia Symptoms: Identifying Abnormal Cell Changes And Seeking Treatment
Cervical Dysplasia: A Silent Threat to Women Everywhere
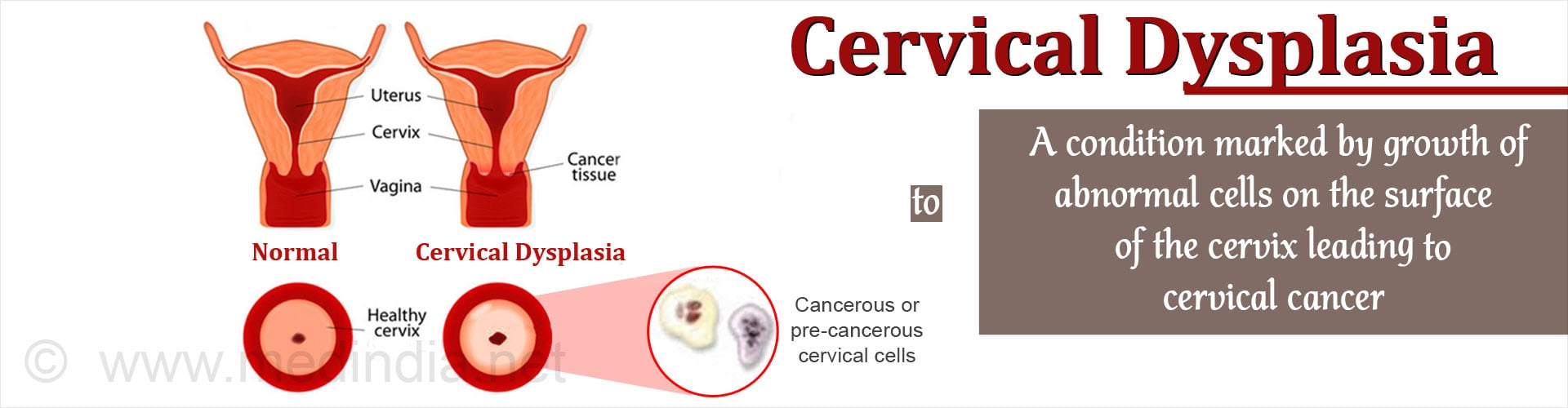
Every year, countless women are diagnosed with cervical dysplasia, a condition that can have serious health implications if left untreated. While many people may not be familiar with this condition, it is a silent threat to women everywhere. In this article, we will help you understand what cervical dysplasia is, how it can affect your health, and what steps you can take to protect yourself from this condition.
Understanding Cervical Dysplasia
Cervical dysplasia is a condition that occurs when abnormal cells in the cervix begin to grow and divide uncontrollably. This condition is typically caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is a sexually transmitted infection. In most cases, the virus is harmless and goes away on its own. However, in some cases, it can lead to the development of cervical dysplasia.
What is Cervical Dysplasia?
Cervical dysplasia is a condition that affects the cells of the cervix, which is the opening to the uterus. When the cells in the cervix begin to grow abnormally, they can form precancerous lesions that can eventually develop into cancer if left untreated.

The Importance of Early Detection and Timely Treatment
Early detection and timely treatment is crucial for women who have been diagnosed with cervical dysplasia. The earlier the condition is detected, the more effective the treatment options are likely to be. In most cases, cervical dysplasia is treated with a procedure called a colposcopy, which allows doctors to examine the cervix and remove any abnormal cells.

Statistics on Cervical Dysplasia
According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 13,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with cervical cancer each year. While this is a relatively small number, it is important to note that cervical dysplasia is a precursor to cervical cancer. This means that early detection and treatment can help prevent the development of cancer.
Types of Cervical Dysplasia
There are several different types of cervical dysplasia, ranging from mild to severe. Mild dysplasia typically goes away on its own without any treatment. Moderate and severe dysplasia, on the other hand, require medical treatment in order to prevent the development of cancer.
Recognizing Early Symptoms of Cervical Dysplasia
In many cases, cervical dysplasia does not cause any symptoms. This is why it is important for women to get regular Pap tests, which can detect the presence of abnormal cells in the cervix. However, some women may experience symptoms such as abnormal bleeding, pain during sex, or abnormal discharge.
Diagnostic Tests for Cervical Dysplasia
If your doctor suspects that you may have cervical dysplasia, they will likely perform a Pap test or a colposcopy. During a Pap test, your doctor will use a small brush to collect cells from your cervix. These cells will then be examined under a microscope to look for any abnormalities. If abnormalities are detected, your doctor will likely perform a colposcopy, which uses a special microscope to examine your cervix in more detail.
The Importance of Awareness and Prevention
Awareness and prevention are key when it comes to protecting yourself from cervical dysplasia. This means getting regular Pap tests, practicing safe sex, and avoiding smoking. It is also important to get vaccinated against HPV, as this can significantly reduce your risk of developing cervical dysplasia.
Support and Resources
If you have been diagnosed with cervical dysplasia, there are many resources available to help you. Support groups can provide valuable emotional support, while organizations such as the National Cervical Cancer Coalition can provide information about treatment options and resources in your area.
While cervical dysplasia can be a scary diagnosis, it is important to remember that with early detection and timely treatment, it is a highly treatable condition. By staying informed and taking the necessary steps to protect yourself, you can help prevent the development of cervical cancer and other serious health complications.
Komentar
Posting Komentar