Chlamydia Treatment In Women: Antibiotics And Partner Notification
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) that affects both men and women. It's caused by the bacterium called chlamydia trachomatis, which can infect the urethra, cervix, rectum, and throat. Chlamydia is spread through unprotected sexual contact with an infected person, and it often has no noticeable symptoms, which makes it easy to spread and hard to detect.
Understanding Chlamydia
Chlamydia is an STD caused by the bacterium called chlamydia trachomatis. It's spread through unprotected sexual contact with an infected person, and it often has no noticeable symptoms. If left untreated, chlamydia can cause serious health problems such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and even ectopic pregnancy.
What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is an STD caused by the bacteria chlamydia trachomatis. It's spread through unprotected sex with an infected person, and it can infect the genitals, rectum, and throat. Chlamydia is one of the most common STDs in the world, and it often goes undetected because it can cause no symptoms.
Importance of chlamydia treatment
Chlamydia is a serious STD that requires prompt treatment to prevent serious health problems and prevent its spread to others. If you believe you have been exposed to chlamydia or are experiencing symptoms, it's important to see a healthcare provider as soon as possible for testing and treatment. Prompt treatment with antibiotics can cure chlamydia and prevent its spread to others, but if left untreated, chlamydia can cause serious health problems such as infertility, PID, and even ectopic pregnancy.
Statistics on chlamydia
Chlamydia is one of the most common STDs in the world, with an estimated 131 million new cases each year. In the United States alone, there were over 1.7 million reported cases of chlamydia in 2018, making it the most commonly reported STD in the country.
Types of chlamydia
There are two main types of chlamydia: genital chlamydia and ocular chlamydia. Genital chlamydia is the most common type and is spread through unprotected sexual contact with an infected person. Ocular chlamydia is less common and is usually spread through hand-to-eye transmission or contact with contaminated surfaces.
Risk factors for chlamydia
Anyone who is sexually active can contract chlamydia, but some people are at higher risk than others. Risk factors for chlamydia include:
- Young age (under 25)
- Multiple sexual partners
- Unprotected sex
- Previous STD diagnosis
- Illicit drug use
Recognizing early symptoms of chlamydia
Chlamydia often has no noticeable symptoms, which makes it easy to spread and hard to detect. However, some people may experience early symptoms of chlamydia, including:
- Painful urination
- Abnormal vaginal or penile discharge
- Pain during sex
- Rectal pain or discharge
- Sore throat
Diagnostic tests for chlamydia
If you believe you have been exposed to chlamydia or are experiencing symptoms, it's important to see a healthcare provider for testing. Diagnostic tests for chlamydia include urine tests, swab tests, and blood tests. These tests can detect the presence of chlamydia in the body, even if you have no symptoms.
Awareness and prevention of chlamydia
Prevention is key when it comes to chlamydia. The best way to prevent chlamydia is to practice safe sex by using condoms or dental dams during sexual contact, being monogamous, and getting tested regularly. Raising awareness of the risks of chlamydia is also important in preventing its spread.
Early detection of chlamydia
Early detection of chlamydia is vital for prompt treatment and preventing the spread of this STD to others. If you believe you have been exposed to chlamydia or are experiencing symptoms, it's important to see a healthcare provider as soon as possible for testing.
Timely treatment for chlamydia
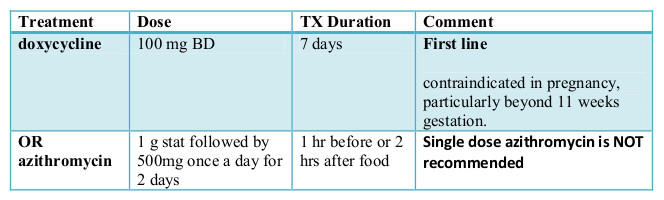
Chlamydia is a serious STD that requires prompt treatment to prevent serious health problems and prevent its spread to others. If you test positive for chlamydia, your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics such as azithromycin or doxycycline to cure the infection. It's important to take all of the prescribed medication and follow your healthcare provider's instructions for preventing the spread of chlamydia to others.
Support and resources for chlamydia treatment
If you have been diagnosed with chlamydia, there are resources available to help you through the treatment process. Contact your healthcare provider or local health department for information on support and resources in your area.
Images:
5 HOME REMEDIES FOR CHLAMYDIA TREATMENT II

Chlamydia Treatment | LloydsPharmacy Online Doctor UK
How Long To Wait After Chlamydia Treatment - Captions Like
Treatment of chlamydia: antibiotics, schemes for men and women - Medical diagnosis
Buy Chlamydia Antibiotics for Chlamydia Treatment

Komentar
Posting Komentar