Chlamydia In Women: Symptoms
Yo, did you hear about Chlamydia? If you don't know what it is, let me school you real quick. Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that affects both men and women. It's caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis and is one of the most common STDs in the United States.
Understanding Chlamydia
Chlamydia is spread through unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the infection. It can also be spread from a mother to her baby during childbirth. Most people who have Chlamydia don't have any symptoms, which makes it easy to spread the infection unknowingly.
What is Chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a curable bacterial infection that affects the genital tract. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, such as infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can cause chronic pain and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancies and infertility in women.
Importance of Getting Tested
Getting tested for Chlamydia is important because it's the only way to know for sure if you have the infection. Testing is quick and easy, and it can be done through a urine test or a swab of the genital area. It's recommended that sexually active women under 25 years old get tested annually for Chlamydia. Men who have sex with men, and people with multiple sexual partners, should also get tested regularly.
Statistics on Chlamydia
Chlamydia is one of the most common STDs in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there were 1.8 million reported cases of Chlamydia in 2018. However, it's estimated that there may be up to 2.86 million new cases of Chlamydia each year, as many people with the infection don't have any symptoms.
Types of Chlamydia
There are two main types of Chlamydia: genital and ocular. Genital Chlamydia is the most common type and affects the genital tract. Ocular Chlamydia affects the eyes and can cause conjunctivitis.
Risk Factors for Chlamydia
Anyone who is sexually active can get Chlamydia, but there are some factors that can increase your risk.
- Having unprotected sex
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Having sex with someone who has multiple sexual partners
- Having sex without a condom
- Having a history of STDs
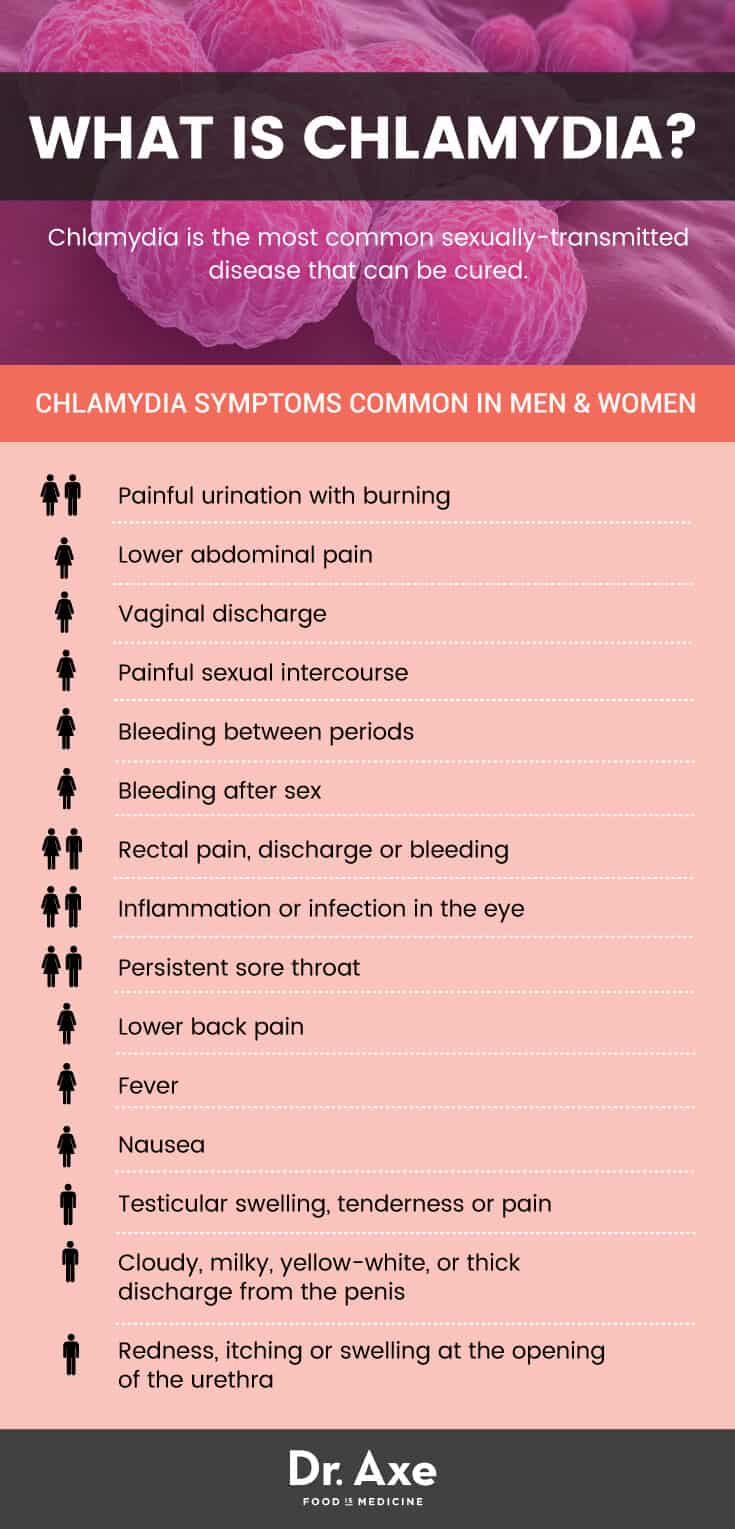
Recognizing Early Symptoms of Chlamydia
As I mentioned earlier, most people with Chlamydia don't have any symptoms. However, if symptoms do occur, they usually show up within one to three weeks after being exposed to the infection. Symptoms in women can include:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Painful urination
- Pain during sex
- Lower abdominal pain
Symptoms in men can include:
- Discharge from the penis
- Painful urination
- Pain and swelling in the testicles
Diagnostic Tests for Chlamydia
If you think you may have Chlamydia, it's important to get tested. Testing is quick and easy and can be done through a urine test or a swab of the genital area.
Awareness and Prevention
Preventing Chlamydia starts with practicing safe sex. This means using a condom every time you have sex, including oral sex. It's also important to limit the number of sexual partners you have and get tested regularly for STDs.
Early Detection is Key
Early detection is key when it comes to treating Chlamydia. If you think you may have the infection, getting tested and treated as soon as possible is important.
Timely Treatment for Chlamydia
Chlamydia is easily treated with antibiotics. If you test positive for Chlamydia, you and your partner will need to take antibiotics to get rid of the infection. It's important to take all of the antibiotics as directed, even if you start feeling better before you finish them.
Support and Resources
If you've been diagnosed with Chlamydia, it's important to know that you're not alone. There are many resources available to help you through this. Your doctor or local health department can provide you with information on support groups and other resources for people with STDs.
The Bottom Line
Chlamydia is a common STD that can cause serious complications if left untreated. The good news is that it's easily prevented and treated. Practicing safe sex, getting tested regularly, and seeking timely treatment if you think you may have an infection are all important steps in protecting your sexual health.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chlamydia-symptoms-5aeca3ffc5542e0036b9ef51.png)

Komentar
Posting Komentar