Uterine Prolapse: Causes
Uterine prolapse is a condition that can affect women of any age. It occurs when the uterus slips from its normal position and protrudes into the vaginal canal. There are several possible causes of uterine prolapse, including weak pelvic floor muscles, pregnancy and childbirth, and hormonal changes in menopause. In this article, we'll explore the different aspects of uterine prolapse, including the types, risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options.
Understanding Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse is a condition where the uterus descends from its original position into the vaginal canal. This condition can result from damage to the connective tissues that support the uterus, which may be due to a variety of causes, including age, pregnancy, and childbirth. A woman with uterine prolapse may experience discomfort, pain, or pressure in the lower pelvic area, and she may also notice a bulge or protrusion in the vagina.

What is Uterine Prolapse?
Uterine prolapse is a condition where the uterus descends from its original position and protrudes into the vaginal canal. There are several possible causes of uterine prolapse, including weak pelvic floor muscles, pregnancy and childbirth, and hormonal changes in menopause. Some women may be more susceptible to uterine prolapse due to genetic or other factors. The condition can be uncomfortable and may cause pain or pressure in the lower pelvic area.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of uterine prolapse can help prevent further damage to the pelvic floor muscles and other structures in the pelvic region. Women who experience symptoms such as discomfort or pain in the pelvic area should seek medical attention as soon as possible. Early detection can also increase the chances of successful treatment and may reduce the risk of complications or more severe symptoms.
Statistics on Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse is a relatively common condition that affects millions of women worldwide. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, up to 50% of women will experience some form of pelvic organ prolapse in their lifetime. Additionally, women who have given birth vaginally are at a higher risk of developing uterine prolapse.
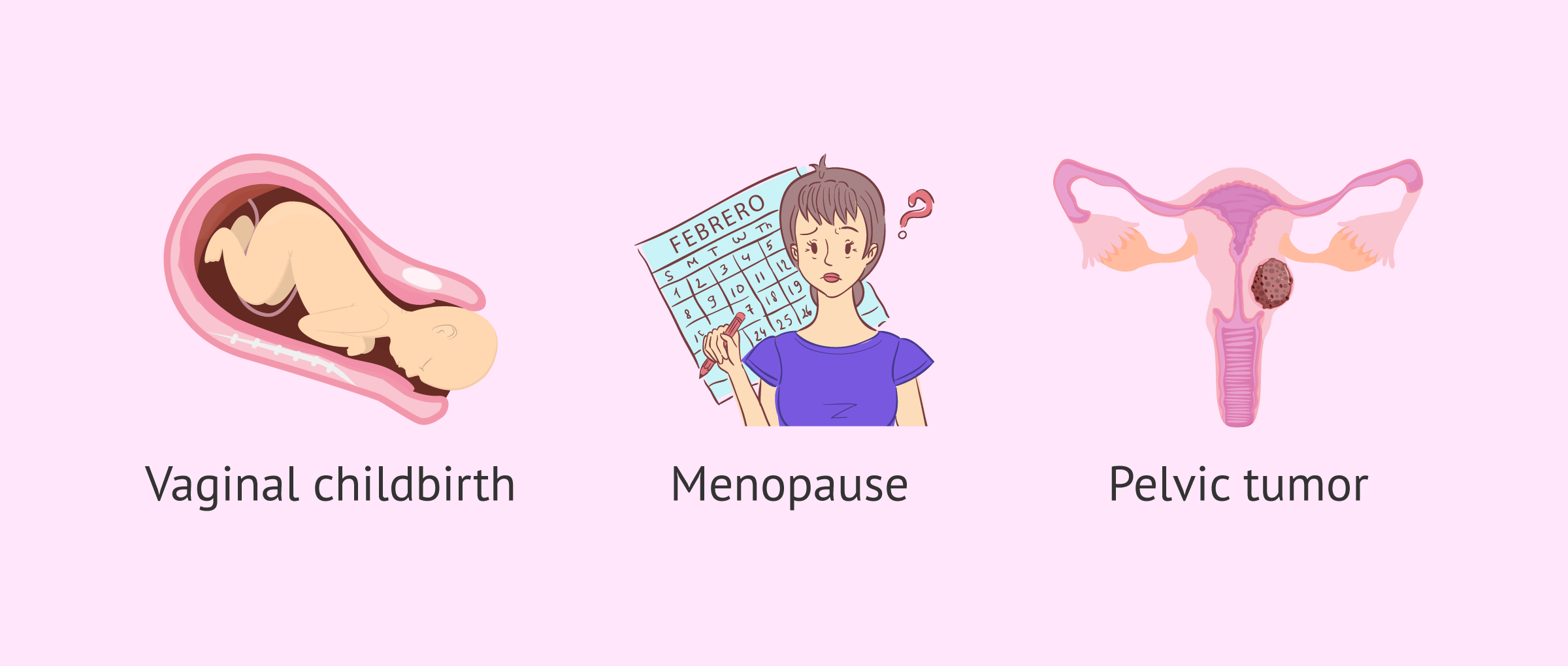
Types of Uterine Prolapse
There are several different types of uterine prolapse, which are classified based on the severity of the condition and the extent of descent of the uterus. The different types of uterine prolapse include first degree, second degree, and third-degree prolapse. First degree prolapse involves a mild descent of the uterus, while third-degree prolapse involves a complete descent of the uterus into the vaginal canal.
Risk Factors for Uterine Prolapse
Several different factors can increase a woman's risk of developing uterine prolapse. These factors include pregnancy and childbirth, age, obesity, chronic constipation, and chronic cough. Women who have a history of pelvic surgery or who have a genetic predisposition to uterine prolapse may also be at a higher risk of developing the condition.
Recognizing Early Symptoms of Uterine Prolapse
Early symptoms of uterine prolapse may include a feeling of pressure or discomfort in the pelvic area, difficulty in urination, and a bulge or protrusion in the vagina. Women who experience these symptoms should seek medical attention as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the pelvic floor muscles and other structures in the pelvic region.
Diagnostic Procedures for Uterine Prolapse
There are several different diagnostic procedures that may be used to diagnose uterine prolapse. These procedures may involve a physical examination, imaging tests such as MRI or ultrasound, or a pelvic exam. Women who are experiencing symptoms of uterine prolapse should consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for diagnosis and treatment.
Awareness and Prevention of Uterine Prolapse
There are several measures that women can take to reduce their risk of developing uterine prolapse. These measures may include maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, practicing good bowel habits, avoiding heavy lifting or straining, and practicing pelvic floor exercises. Additionally, women who are planning to become pregnant or who have recently given birth should consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for reducing the risk of uterine prolapse.
Timely Treatment of Uterine Prolapse
The treatment of uterine prolapse may depend on the severity of the condition and the cause of the prolapse. Treatments may include pelvic floor exercises, medication, hormone replacement therapy, or surgery. Women who are experiencing symptoms of uterine prolapse should consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for treatment.
Support and Resources for Women with Uterine Prolapse
There are several resources available for women who are living with uterine prolapse. These resources may include support groups, online communities, and healthcare professionals who specialize in the treatment of pelvic floor dysfunction. Women who are struggling with the symptoms of uterine prolapse should seek out these resources to help them manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Komentar
Posting Komentar