Vaginitis: Types
Vaginitis and Vulvitis are common conditions that women face. It can be an uncomfortable experience, but it is essential to understand the various types of vaginitis and vulvitis to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Vaginitis
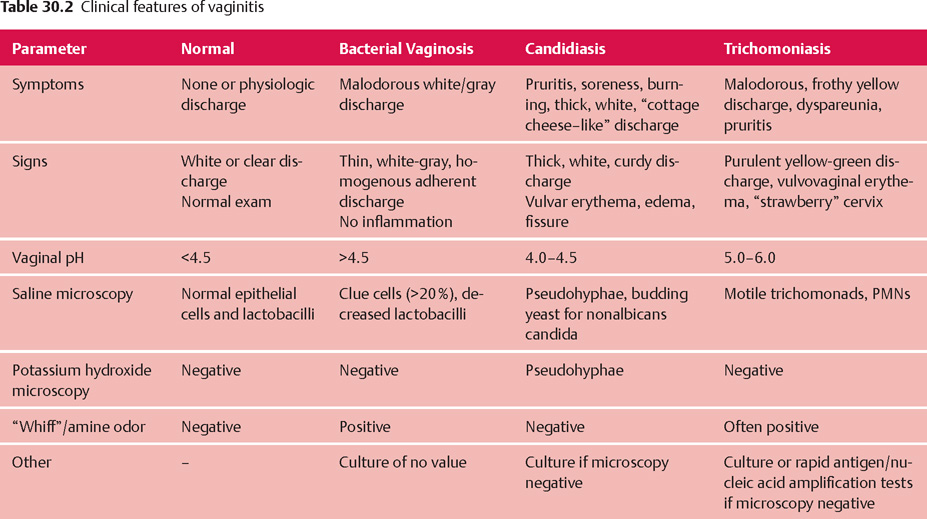
Vaginitis is the inflammation of the vagina that results in an increase of discharge, itching, and discomfort. Bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, trichomoniasis, and atrophic vaginitis are the most common types of vaginitis.
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis, or BV, results from a bacterial imbalance in the vagina. The primary symptom is increased discharge, often with an unpleasant smell. BV is a common condition in women, with an estimated 30% of women in the United States experiencing this condition.

Yeast Infections
Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of yeast in the vagina. The primary symptom is itching, accompanied by a thick white discharge. Yeast infections commonly occur in women who are pregnant or have diabetes.

Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis, often called "trich," is a sexually transmitted infection that results in itching, burning, and discharge. Trichomoniasis is the most common curable sexually transmitted infection in young sexually active women.

Atrophic Vaginitis
Atrophic vaginitis occurs when the vagina starts to thin and dry due to a decrease in estrogen levels. The primary symptom is vaginal dryness and discomfort, especially during sexual intercourse.
Vulvitis
Vulvitis is the inflammation of the external genitalia that is most commonly caused by an infection or allergy. Symptoms of vulvitis include itching, burning, pain, and redness.

Understanding
Vaginitis and vulvitis are two different conditions that can occur simultaneously. These conditions can be uncomfortable and disturbing for women and can affect their sexuality and overall health.
What is
Vaginitis refers to inflammation of the vagina, while vulvitis refers to inflammation of the external genitalia. Both conditions can cause itching, burning, and discharge, but the causes and treatments may differ.
Importance of
It is essential to recognize the symptoms of vaginitis and vulvitis and seek medical attention promptly. Proper diagnosis and treatment can prevent the development of complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease, increased susceptibility to sexually transmitted infections, and even infertility.
Statistics on
Approximately 75% of women will experience at least one episode of vaginitis in their lifetime. Bacterial vaginosis affects approximately 30% of women in the United States. Yeast infections occur in about 75% of women during their lifetime, and trichomoniasis affects 3 million women every year in the United States.
Types of
The most common types of vaginitis are bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, trichomoniasis, and atrophic vaginitis. Vulvitis can be caused by an infection or an allergy, with common types being contact dermatitis and irritant dermatitis.
Risk factors
Risk factors for vaginitis and vulvitis include a weakened immune system, hormonal changes, antibiotic use, pregnancy, and diabetes. Sexual activity, multiple sex partners, and poor hygiene can also increase the risk of developing vaginitis or vulvitis.
Recognizing Early Symptoms of
Early symptoms of vaginitis and vulvitis include itching, burning, and discharge. Vaginitis can also result in pain during sex, while vulvitis can cause pain or discomfort when wearing tight clothing or during exercise.
Diagnostic
Diagnosis of vaginitis and vulvitis can be made through a physical examination, laboratory testing of vaginal and vulvar samples, and vaginal pH testing.
Awareness and Prevention
Avoiding irritants, such as perfumed products, and practicing good hygiene can help prevent vulvitis. Proper use of barrier protection during sexual activity can also reduce the risk of developing vaginitis and trichomoniasis. Antibiotic use should be reserved for a bacterial infection diagnosed by a healthcare professional.
Early Detection
Early detection of vaginitis and vulvitis can prevent complications and make treatment more effective. Women should be aware of any changes in vaginal discharge, itching, or burning and seek medical attention promptly.
Timely Treatment
Treatment for vaginitis and vulvitis is dependent on the underlying cause. Bacterial vaginosis is treated with antibiotics, while yeast infections can be treated with over-the-counter antifungal medications. Trichomoniasis requires prescription medication, and atrophic vaginitis can be treated with hormone supplements or topical estrogen preparations.
Support and Resources
Women experiencing vaginitis or vulvitis can seek support and resources from a healthcare professional. Health organizations, such as the American Sexual Health Association, provide education and resources for women experiencing these conditions.
Komentar
Posting Komentar